Quick Reference Psychosomatic Medicine
Abstract
Source: Sandson NB, Armstrong SC, Cozza KL: Med-Psych Drug-Drug Interactions Update An Overview of Psychotropic Drug-Drug Interactions. Psychosomatics 2005;46:464–494. Reprinted with permission. Please refer to the full article for specific citations of each interaction.
The psychotropic drug-drug interactions most likely to be relevant to psychiatrists' practices are examined. The metabolism and the enzymatic and P-glycoprotein inhibition/induction profiles of all antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers are described; all clinically meaningful drug-drug interactions between agents in these psychotropic classes, as well as with frequently encountered nonpsychotropic agents, are detailed; and information on the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic results, mechanisms, and clinical consequences of these interactions is presented. Although the range of drug-drug interactions involving psychotropic agents is large, it is a finite and manageable subset of the much larger domain of all possible drug-drug interactions. Sophisticated computer programs will ultimately provide the best means of avoiding drug-drug interactions. Until these programs are developed, the best defense against drug-drug interactions is awareness and focused attention to this issue.

Appendix 1. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Antidepressants
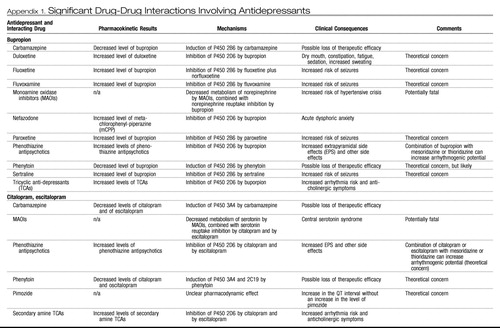 |
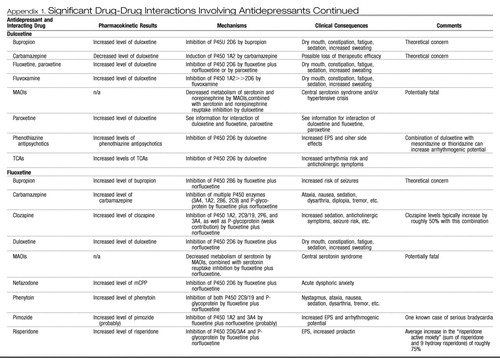 |
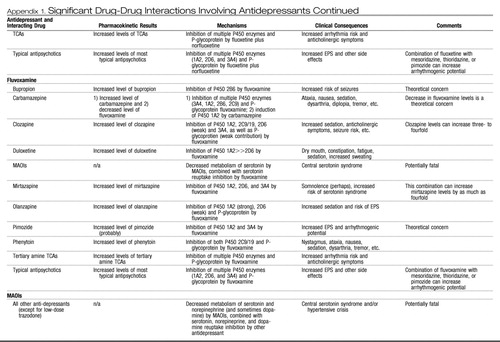 |
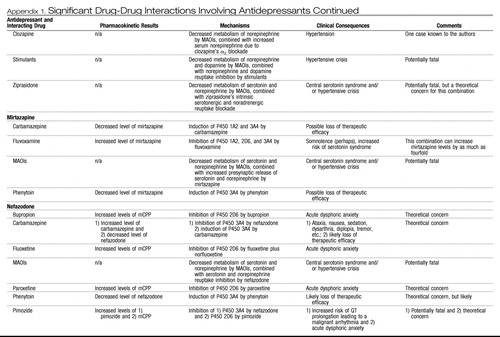 |
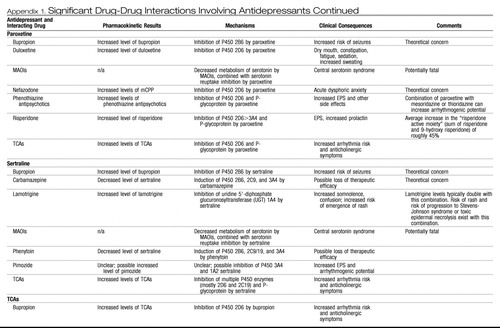 |
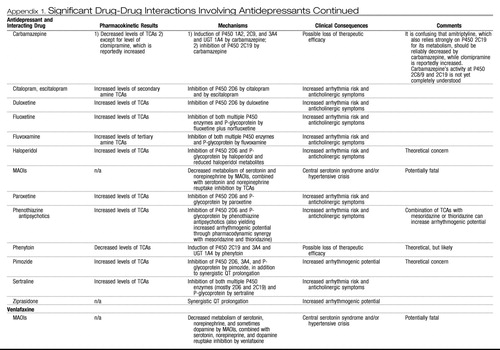 |
Appendix 1. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Antidepressants
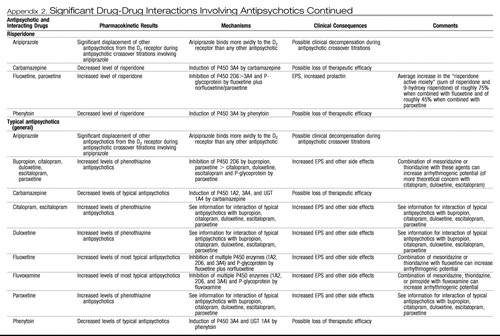
Appendix 2. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Antipsychotics
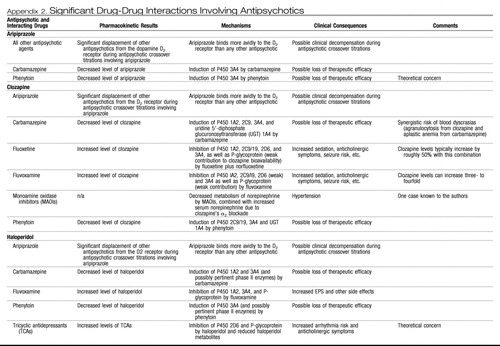 |
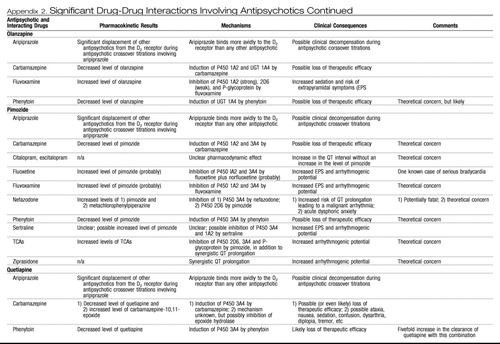 |
 |
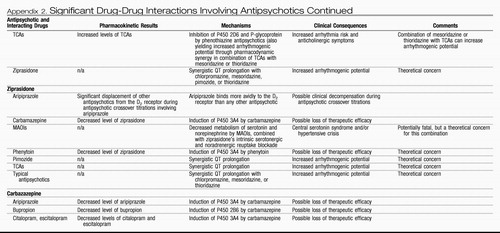 |
Appendix 2. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Antipsychotics
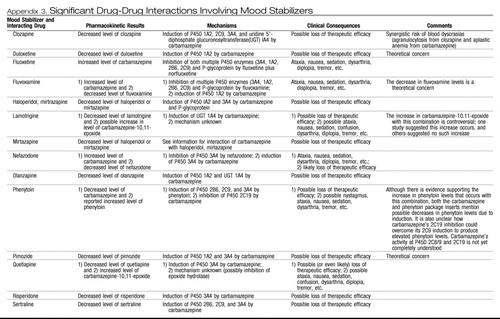
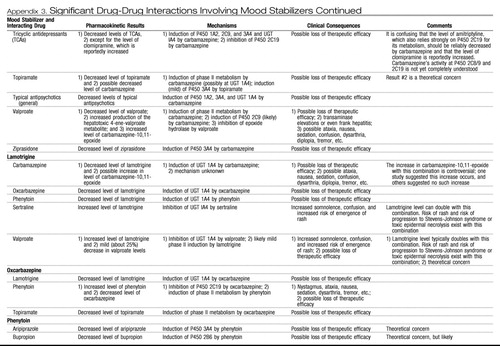
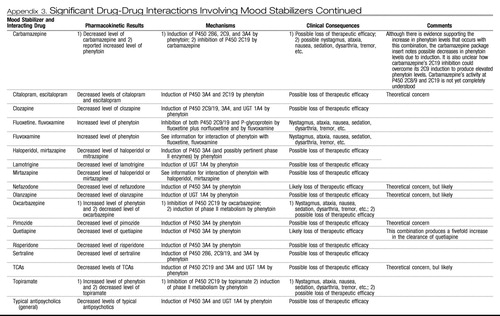
Appendix 3. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Mood Stabilizers
 |
 |
 |
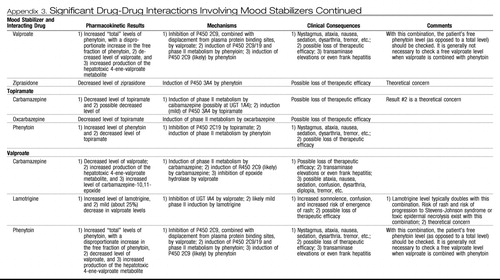 |
Appendix 3. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Mood Stabilizers
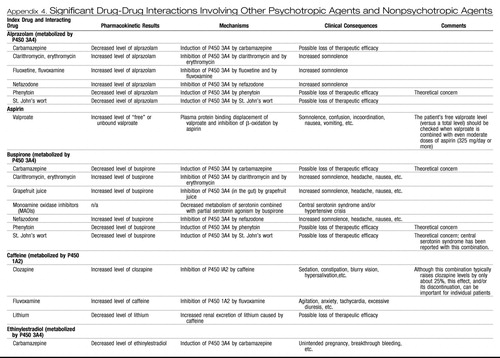
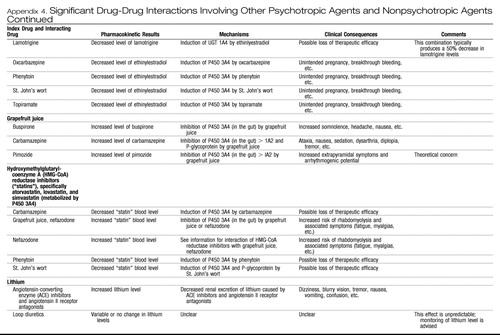
Appendix 4. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Other Psychotropic Agents and Nonpsychotropic Agents
 |
 |
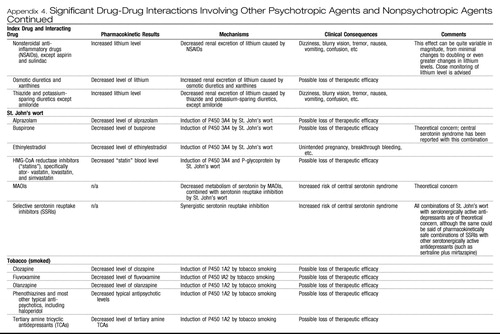 |
Appendix 4. Significant Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Other Psychotropic Agents and Nonpsychotropic Agents



